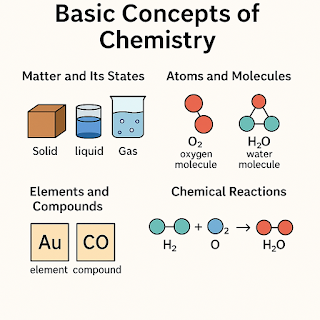
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
Chemistry is the branch of science that deals with the composition, structure, properties, and changes of matter. To understand more advanced topics in chemistry, it’s essential to grasp its foundational concepts. Let’s dive into some of the most important basic ideas.
1. Matter and Its Classification
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. It exists in different forms like solids, liquids, and gases.
Types of Matter:
- Pure Substances: Elements and compounds
- Mixtures: Homogeneous (solutions) and heterogeneous mixtures
Image Suggestion: A simple diagram showing solid, liquid, and gas; a comparison between pure substances and mixtures.
2. Properties of Matter
Physical Properties
- Can be observed without changing the identity of the substance.
- Examples: color, boiling point, melting point, density
Chemical Properties
- Involve a change in the chemical identity.
- Examples: flammability, reactivity with acid
Image Suggestion: Table or chart comparing physical vs chemical properties.
3. Measurement and Units
Chemistry relies heavily on accurate measurements. The SI (International System of Units) is used for standardization.
Common SI Units in Chemistry:
- Length: meter (m)
- Mass: kilogram (kg)
- Time: second (s)
- Amount of substance: mole (mol)
- Temperature: kelvin (K)
Image Suggestion: Infographic of SI base units with symbols and examples.
4. The Mole Concept
The mole is a fundamental concept used to count entities at the atomic level.
- 1 mole = 6.022 × 10²³ particles (Avogadro’s Number)
- Used to relate the mass of a substance to the number of atoms or molecules.
Image Suggestion: Diagram illustrating 1 mole of different substances (e.g., 1 mol of H₂O = 18g).
5. Atomic and Molecular Mass
- Atomic mass: The mass of a single atom (in atomic mass units, u or amu)
- Molecular mass: Sum of atomic masses in a molecule
Example: Molecular mass of H₂O = 2(1) + 16 = 18 u
Image Suggestion: Water molecule with labeled atomic masses.
6. Laws of Chemical Combination
a. Law of Conservation of Mass
Mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
b. Law of Definite Proportions
A compound always contains the same elements in the same proportion by mass.
c. Law of Multiple Proportions
When two elements combine to form more than one compound, the mass ratios are simple whole numbers.
Image Suggestion: Balanced chemical reaction showing conservation of mass; visual comparison of CO and CO₂ for multiple proportions.
7. Empirical and Molecular Formula
- Empirical formula: The simplest whole-number ratio of atoms
- Molecular formula: Actual number of atoms in a molecule
Example:
Glucose
- Empirical formula: CH₂O
- Molecular formula: C₆H₁₂O₆
Image Suggestion: Side-by-side depiction of molecular vs empirical formulas.
Conclusion
Understanding these fundamental concepts is the first step in mastering chemistry. They lay the groundwork for everything from chemical reactions to complex industrial processes.
Want more visuals? Let me know, and I can generate custom educational diagrams or infographics for each section!